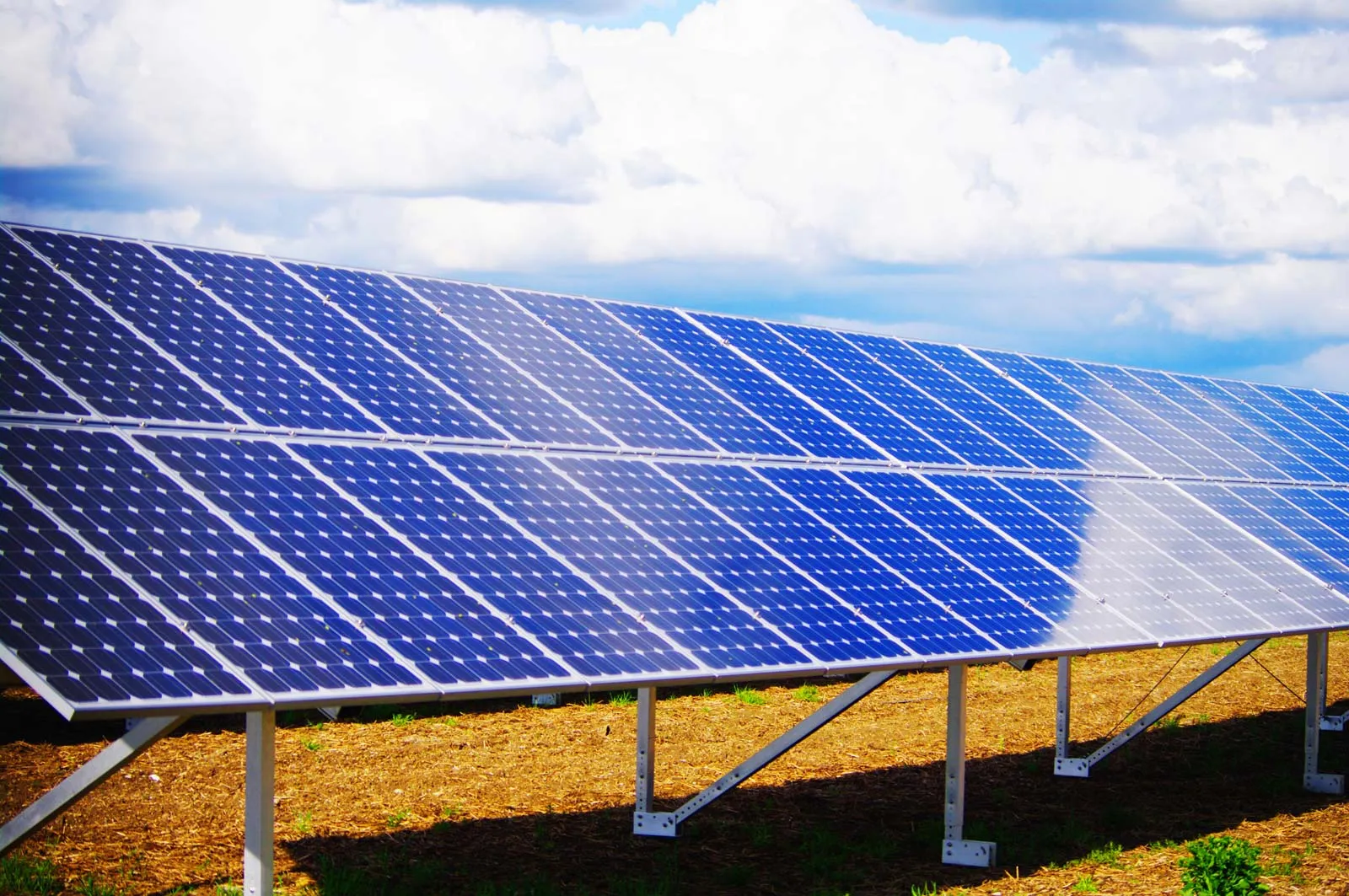
In the pursuit of sustainable energy sources, the marriage of agriculture and renewable energy has emerged as a promising alliance. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and the need for clean energy, renting agricultural affitta terreno fotovoltaico land for photovoltaic (PV) projects has become a compelling solution. This unique synergy not only offers farmers an additional revenue stream but also contributes to the global shift towards a greener future.
The Dual Purpose of Agricultural Land:
Traditionally, agricultural land has been viewed through a single lens – a canvas for growing crops and sustaining livelihoods. However, the changing landscape of energy demands has paved the way for a dual-purpose utilization of these vast expanses. By integrating solar panels into agricultural fields, farmers can now harness the sun’s energy while continuing to cultivate the land beneath.
Financial Benefits for Farmers:
One of the primary incentives for farmers to engage in the rental of their land for photovoltaic projects is the financial boon it brings. With the uncertainty associated with traditional farming practices, solar leasing provides a stable and consistent income. The revenue generated from leasing land for solar projects not only acts as a supplementary income but also serves as a hedge against the unpredictability of agricultural yields and market fluctuations.
Additionally, government incentives and subsidies aimed at promoting renewable energy adoption further sweeten the deal for farmers. These financial benefits make the integration of photovoltaic systems an attractive proposition for agricultural landowners, creating a win-win situation for both the farming community and the renewable energy sector.
Sustainable Land Use Practices:
The coexistence of agriculture and solar power is not just about financial gains; it also embodies a commitment to sustainable land use practices. Integrating solar panels into agricultural landscapes allows for the efficient utilization of available space, minimizing the environmental impact associated with large-scale solar installations in non-agricultural areas.
This dual land use approach, known as agrivoltaics, promotes resource efficiency by optimizing sunlight exposure for both crops and solar panels. Studies have shown that the shade provided by solar panels can reduce water evaporation, creating a microclimate that benefits certain crops. This harmonious relationship fosters a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to land management.
Addressing Concerns and Challenges:
While the idea of leasing agricultural land for photovoltaic ventures is promising, it is not without its challenges. One concern is the potential displacement of crops due to the shading effects of solar panels. To address this, strategic planning and technological advancements, such as elevated solar arrays, can be implemented to allow sunlight penetration for crops.
Furthermore, there is a need for clear and comprehensive leasing agreements that address issues such as land restoration post-lease and the responsibilities of both parties involved. Collaborative efforts between farmers, energy companies, and policymakers are essential to establish guidelines that ensure the long-term sustainability of such ventures.
Community Engagement and Support:
The success of agricultural land rental for photovoltaic projects relies heavily on community engagement and support. Open communication channels between farmers, local communities, and renewable energy developers can foster understanding and address concerns. Community involvement can also lead to shared benefits, such as job creation, educational programs, and the establishment of local renewable energy infrastructure.
In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources, the agricultural landscape is undergoing a transformation. Farmers and landowners are increasingly exploring the prospect of leasing their agricultural land for the installation of photovoltaic (PV) systems. This novel approach not only provides an additional revenue stream for landowners but also contributes to the global shift towards clean energy. This article delves into the dynamics, benefits, and challenges of renting agricultural land for photovoltaic projects.
The Marriage of Agriculture and Solar Power:
Traditionally, agricultural land has been utilized for food production, but the intersection of agriculture and renewable energy is creating new opportunities. Photovoltaic technology, which converts sunlight into electricity, has proven to be a sustainable and economically viable energy solution. By harnessing the sun’s energy, photovoltaic farms can generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
Conclusion:
The rental of agricultural land for photovoltaic ventures represents a transformative approach to land use, blending the traditional with the innovative. As the world races towards a more sustainable future, this dual-purpose utilization of land not only addresses the pressing need for clean energy but also offers farmers a resilient source of income. By fostering collaboration between the agricultural and renewable energy sectors, we can create a blueprint for a greener, more sustainable world, where the sun’s energy powers not only our homes and industries but also the growth of our crops.
In the pursuit of sustainable energy sources, the marriage of agriculture and renewable energy has emerged as a promising alliance. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and the need for clean energy, renting agricultural land for photovoltaic (PV) projects has become a compelling solution. This unique synergy not only offers farmers an additional revenue stream but also contributes to the global shift towards a greener future.
The Dual Purpose of Agricultural Land:
Traditionally, agricultural land has been viewed through a single lens – a canvas for growing crops and sustaining livelihoods. However, the changing landscape of energy demands has paved the way for a dual-purpose utilization of these vast expanses. By integrating solar panels into agricultural fields, farmers can now harness the sun’s energy while continuing to cultivate the land beneath.
Financial Benefits for Farmers:
One of the primary incentives for farmers to engage in the rental of their land for photovoltaic projects is the financial boon it brings. With the uncertainty associated with traditional farming practices, solar leasing provides a stable and consistent income. The revenue generated from leasing land for solar projects not only acts as a supplementary income but also serves as a hedge against the unpredictability of agricultural yields and market fluctuations.
Additionally, government incentives and subsidies aimed at promoting renewable energy adoption further sweeten the deal for farmers. These financial benefits make the integration of photovoltaic systems an attractive proposition for agricultural landowners, creating a win-win situation for both the farming community and the renewable energy sector.
Sustainable Land Use Practices:
The coexistence of agriculture and solar power is not just about financial gains; it also embodies a commitment to sustainable land use practices. Integrating solar panels into agricultural landscapes allows for the efficient utilization of available space, minimizing the environmental impact associated with large-scale solar installations in non-agricultural areas.
This dual land use approach, known as agrivoltaics, promotes resource efficiency by optimizing sunlight exposure for both crops and solar panels. Studies have shown that the shade provided by solar panels can reduce water evaporation, creating a microclimate that benefits certain crops. This harmonious relationship fosters a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to land management.
Addressing Concerns and Challenges:
While the idea of leasing agricultural land for photovoltaic ventures is promising, it is not without its challenges. One concern is the potential displacement of crops due to the shading effects of solar panels. To address this, strategic planning and technological advancements, such as elevated solar arrays, can be implemented to allow sunlight penetration for crops.
Furthermore, there is a need for clear and comprehensive leasing agreements that address issues such as land restoration post-lease and the responsibilities of both parties involved. Collaborative efforts between farmers, energy companies, and policymakers are essential to establish guidelines that ensure the long-term sustainability of such ventures.
Community Engagement and Support:
The success of agricultural land rental for photovoltaic projects relies heavily on community engagement and support. Open communication channels between farmers, local communities, and renewable energy developers can foster understanding and address concerns. Community involvement can also lead to shared benefits, such as job creation, educational programs, and the establishment of local renewable energy infrastructure.
In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources, the agricultural landscape is undergoing a transformation. Farmers and landowners are increasingly exploring the prospect of leasing their agricultural land for the installation of photovoltaic (PV) systems. This novel approach not only provides an additional revenue stream for landowners but also contributes to the global shift towards clean energy. This article delves into the dynamics, benefits, and challenges of renting agricultural land for photovoltaic projects.
The Marriage of Agriculture and Solar Power:
Traditionally, agricultural land has been utilized for food production, but the intersection of agriculture and renewable energy is creating new opportunities. Photovoltaic technology, which converts sunlight into electricity, has proven to be a sustainable and economically viable energy solution. By harnessing the sun’s energy, photovoltaic farms can generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.