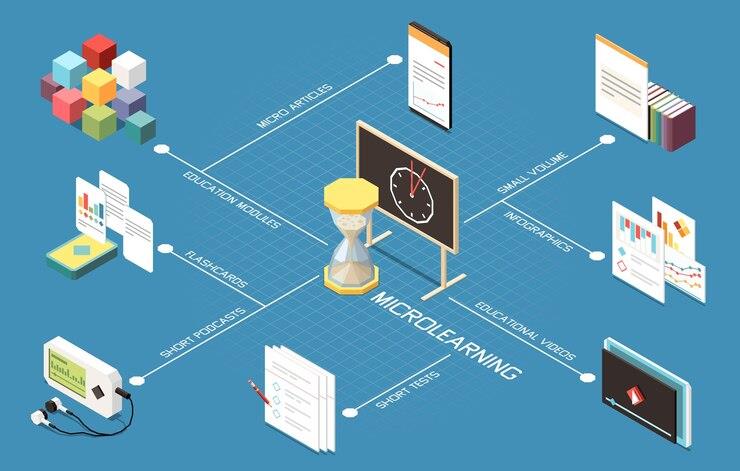
In the ever-evolving landscape of education and corporate training, microlearning has emerged as a transformative approach, revolutionizing the way individuals acquire knowledge.
The different types of microlearning encompass concise learning modules designed to meet the needs of today’s fast-paced learners.
As the demand for flexible and efficient training solutions grows, the significance of microlearning becomes increasingly evident.
Whether in educational institutions or corporate settings, its ability to deliver targeted, bite-sized content aligns perfectly with the modern learner’s preferences.
Join us as we delve into the world of Microlearning, exploring its types and strategies, and unlocking the advantages it brings within the realm of Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Understanding Learning Management Systems
In the contemporary landscape of education and corporate training, Learning Management Systems stand as the bedrock of efficient and organized learning experiences.
Overview of Learning Management Systems
Learning Management Systems are comprehensive platforms designed to streamline, deliver, and manage educational content in diverse settings.
They encompass a range of features, including content creation, administration, tracking, and reporting, creating a centralized hub for learning resources.
The Pivotal Role of LMS in Modern Learning Environments
LMS plays a pivotal role by providing a structured framework for learning content, facilitating seamless access to resources, and offering tools for assessment and feedback.
In the dynamic landscape of modern learning, LMS acts as a catalyst for collaboration, personalization, and data-driven decision-making, ensuring that learners and educators alike can harness the full potential of educational technology for optimal outcomes.
Understanding Microlearning
Microlearning involves the delivery of brief, targeted learning units that concentrate on a specific learning objective.
These bite-sized modules, often ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes, are designed for quick consumption, catering to the contemporary learner’s preference for concise, on-the-go education.
Microlearning can take various forms, including videos, quizzes, infographics, and short articles, providing flexibility in content delivery.
Key Benefits of Microlearning in Training Programs
- Efficiency and Flexibility: Microlearning optimizes time and resources by focusing on one learning objective at a time, allowing learners to access information when and where they need it.
- Improved Retention: The condensed nature of microlearning content enhances information retention, as learners can absorb and apply knowledge in a more targeted manner.
- Engagement and Accessibility: Bite-sized modules cater to shorter attention spans, ensuring higher engagement levels. Additionally, the accessibility of microlearning content on various devices supports seamless learning experiences.
- Adaptability: Microlearning adapts well to different learning styles and preferences, providing a versatile solution for a diverse audience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The modular nature of microlearning reduces development costs and makes content updates more manageable, contributing to overall cost-effectiveness in training programs.
Types of Microlearning
1. Bite-sized Learning
Bite-sized learning, a cornerstone of microlearning, is characterized by its concise and focused approach. It involves delivering small, easily digestible units of information that concentrate on a specific learning objective.
These units are designed to be consumed in a short amount of time, typically ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes. The essence of bite-sized learning lies in its ability to provide relevant and targeted content, maximizing learner engagement and retention.
Real-world Examples
- Language Learning Apps: Platforms like Duolingo and Babbel utilize bite-sized learning modules, offering users short lessons focused on specific vocabulary or grammar rules.
- Product Training Videos: Companies often use brief, targeted videos to train employees on product features or updates, ensuring efficient and accessible learning.
- Daily Tips or Facts: Educational apps or websites providing daily tips or facts follow the bite-sized learning model, delivering concise information regularly.
- Safety Training Snippets: In industries with strict safety protocols, bite-sized learning modules covering specific safety procedures are common, ensuring that employees can quickly absorb and apply crucial information.
Bite-sized Learning’s efficiency and adaptability make it a versatile and impactful approach in a variety of learning contexts.
2. Interactive Modules
Interactive modules in microlearning play a crucial role in elevating engagement levels by fostering active participation and hands-on learning experiences. Incorporating engagement involves the strategic use of interactive elements within the learning content.
This can include interactive quizzes, simulations, branching scenarios, and gamified elements, prompting learners to actively participate in the learning process. By creating an immersive and participatory environment, interactive modules enhance knowledge retention and application.
Best Practices for Interactive Modules
- Align with Learning Objectives: Ensure that interactive elements directly align with the learning objectives, reinforcing key concepts and skills.
- User-Friendly Design: Keep interfaces intuitive and user-friendly to avoid distractions and ensure a seamless learning experience.
- Varied Interactivity Levels: Integrate a mix of interactive elements, catering to different learning styles and preferences.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Provide immediate feedback on learner responses to reinforce correct answers or guide learners in understanding misconceptions.
- Gamification Elements: Incorporate gamification aspects, such as badges, points, or leaderboard features, to enhance motivation and competition.
- Mobile Compatibility: Ensure that interactive modules are responsive and accessible across various devices, supporting on-the-go learning.
- Interactive modules not only enhance engagement but also transform microlearning into a dynamic and effective tool for skill development and knowledge acquisition.
3. Multimedia Infusion
Multimedia infusion in microlearning involves integrating various forms of media, such as images, videos, audio, and interactive elements, to enrich the learning experience.
This approach recognizes that individuals have diverse learning preferences, and multimedia elements cater to visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners.
By leveraging multimedia, microlearning transforms into a dynamic, engaging, and multi-sensory experience, fostering better understanding and retention of information.
Case Studies Demonstrating Multimedia Effectiveness
- Language Learning Apps: Platforms like Rosetta Stone use multimedia elements, combining visuals, audio, and interactive exercises to teach language skills effectively.
- Technical Training Videos: In industries requiring hands-on skills, multimedia-infused microlearning includes instructional videos demonstrating step-by-step procedures, enhancing comprehension.
- Corporate Compliance Training: Multimedia elements, such as scenario-based videos and interactive simulations, effectively communicate complex compliance regulations, making training more accessible.
- Health and Safety E-learning: Animated videos, infographics, and interactive scenarios in microlearning modules enhance understanding and compliance with health and safety protocols in various workplaces.
Multimedia infusion in microlearning not only caters to diverse learning styles but also brings real-world scenarios to life, creating a compelling and memorable learning experience.
Strategic Integration with LMS
Integrating Microlearning with a Learning Management System requires a systematic approach to ensure a smooth and effective implementation.
- Needs Assessment: Identify specific learning objectives and target audiences to tailor microlearning content accordingly.
- Content Creation: Develop concise and targeted microlearning modules aligned with identified learning goals.
- LMS Compatibility Check: Ensure that the chosen microlearning content format is compatible with the features and capabilities of the LMS.
- Metadata Tagging: Implement effective metadata tagging to categorize and organize microlearning content within the LMS.
- User Access and Permissions: Configure LMS settings to control user access, ensuring that learners can easily locate and engage with microlearning modules.
- Testing and Feedback: Conduct thorough testing to identify and address any technical issues, and gather feedback from pilot users to refine the integration.
Overcoming Common Integration Challenges
Despite the benefits, integrating microlearning with LMS may encounter challenges, including:
- Technical Compatibility: Address issues related to different file formats, multimedia compatibility, and responsive design.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive microlearning content and user data.
- User Adoption: Provide clear instructions and support to ensure that learners are comfortable navigating the integrated microlearning content.
- Content Updates: Establish a streamlined process for updating and refreshing microlearning content within the LMS.
By following these steps and proactively addressing potential challenges, organizations can seamlessly integrate microlearning into their LMS, maximizing its impact on learning outcomes.
Tracking and Analytics
Utilizing the capabilities of a Learning Management System for monitoring microlearning progress is essential for gauging effectiveness and learner engagement.
- User Progress Tracking: LMS platforms enable real-time tracking of individual learner progress through microlearning modules, providing insights into completion rates and areas where learners may need additional support.
- Assessment Data: Assessments within microlearning modules generate data on learner performance, helping to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
- Engagement Metrics: Tracking user interactions, such as time spent on modules and frequency of logins, offers valuable indicators of overall engagement.
Importance of Analytics in Optimizing Microlearning Strategies
- Personalization: Analytics help identify individual learner preferences, allowing for the customization of microlearning content to match specific needs and learning styles.
- Content Effectiveness: Analytics reveal which microlearning modules are most effective, allowing organizations to refine and enhance content for better learning outcomes.
- Identifying Trends: Analyzing data trends helps uncover patterns in learner behavior, allowing organizations to stay ahead of evolving training needs and preferences.
- ROI Assessment: By tracking the impact of microlearning on performance metrics, organizations can assess the return on investment (ROI) and make data-driven decisions for future strategies.
- Leveraging tracking and analytics within the LMS not only provides valuable insights into microlearning effectiveness but also empowers organizations to continually refine and optimize their microlearning strategies for maximum impact.
Future Trends
As the educational and corporate landscapes continue to evolve, several future trends are poised to shape the integration of Microlearning and Learning Management Systems revolutionizing the learning experience.
AI-Driven Personalization
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within LMS platforms will enable highly personalized Microlearning experiences. AI algorithms will analyze learner data to recommend tailored microlearning content, catering to individual preferences and learning styles.
Immersive Technologies Integration
The incorporation of immersive technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) within Microlearning modules, facilitated by LMS integration, will provide learners with interactive and realistic learning experiences, enhancing engagement and knowledge retention.
Adaptive Learning Paths
Future LMS and Microlearning integrations will feature adaptive learning paths. AI algorithms will dynamically adjust the sequence and content of microlearning modules based on individual learner progress, ensuring a personalized and optimized learning journey.
Social Learning Integration
LMS platforms will increasingly integrate social learning features into Microlearning, fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing among learners. Social elements such as discussion forums, peer reviews, and collaborative projects will enhance the overall learning experience.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Enhanced analytics capabilities within LMS platforms will enable more sophisticated data-driven decision-making. Organizations will leverage comprehensive data insights to continually refine and optimize Microlearning strategies, aligning them with evolving learner needs.
Mobile-First Approach
With the growing reliance on mobile devices, future trends in Microlearning and LMS integration will prioritize a mobile-first approach. Microlearning content will be designed and optimized for seamless access and engagement on various mobile devices.
Continuous Learning Culture
The integration of Microlearning with LMS will contribute to fostering a continuous learning culture within organizations. Learners will have access to bite-sized, relevant content whenever they need it, promoting ongoing skill development and knowledge acquisition.
Blockchain for Credentialing
Blockchain technology may play a role in secure credentialing for Microlearning achievements. Learners could receive verifiable digital badges or certificates through blockchain, adding an extra layer of trust and authenticity to their acquired skills.
As Microlearning and LMS integration continues to evolve, these emerging trends signify a dynamic future where technology and learning seamlessly converge, offering learners and organizations innovative and effective ways to navigate the educational landscape.
Conclusion
The dynamic integration of Microlearning with Learning Management Systems is at the forefront of educational innovation. As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape, embracing trends like AI-driven personalization, immersive technologies, and adaptive learning paths, we pave the way for a future where learning is not only efficient but tailored to individual needs.
The collaborative synergy of Microlearning and LMS heralds a continuous learning culture, leveraging data-driven insights and emerging technologies to redefine the way knowledge is acquired and applied. The journey ahead holds exciting prospects, promising a transformative and personalized learning experience for learners and organizations alike.