Navigating the Blue Economy: Exploring the Vast Potential of Our Oceans
In a world where environmental concerns and sustainable practices have taken center stage, the concept of the “Blue Economy” has emerged as a beacon of hope for our planet’s future. As we strive to strike a balance between economic growth and ecological preservation, the Blue Economy offers a unique perspective by focusing on the sustainable utilization of ocean resources. In this extended blog, we delve into what the Blue Economy is, its significance, and the myriad opportunities it presents for a brighter and more sustainable future.

Understanding the Blue Economy
The concept of the Blue Economy has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential solution to the challenges of environmental degradation, economic inequality, and resource depletion. But what exactly is the Blue Economy, and how does it differ from traditional economic models? In this section, we will delve deeper into the core principles and components of the Blue Economy.
Defining the Blue Economy
At its core, the Blue Economy is an economic framework that places the well-being of both people and the planet at its center. Unlike the traditional economy, which often prioritizes short-term profit and growth at the expense of long-term sustainability, the Blue Economy seeks to balance economic advancement with ecological preservation.
The Blue Economy recognizes the immense value of our oceans and their resources, emphasizing the sustainable use of marine ecosystems to promote economic development, improve livelihoods, and ensure the health of our planet. It encompasses a wide range of sectors, from traditional activities like fishing and shipping to emerging fields such as marine biotechnology and renewable energy.
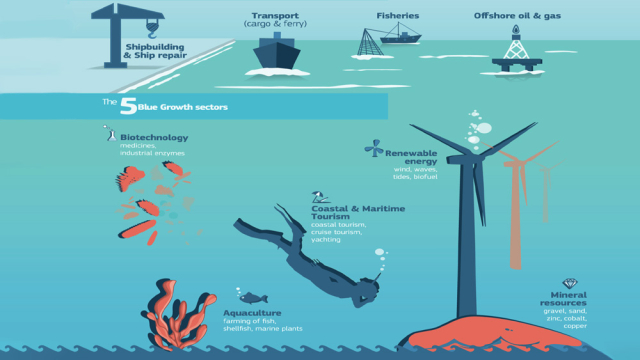
Components of the Blue Economy
The Blue Economy consists of several key components, each contributing to its overall framework:
- Sustainable Fisheries and Aquaculture: The responsible management of fish stocks and the development of sustainable aquaculture practices are central to the Blue Economy. By preventing overfishing and promoting responsible harvesting, we can ensure the long-term availability of seafood resources.
- Marine Renewable Energy: The Blue Economy leverages the power of the oceans to generate clean energy. Offshore wind farms, tidal energy converters, and wave energy systems are examples of how marine resources can contribute to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
- Tourism and Recreation: Coastal and marine tourism can drive economic growth in coastal communities while fostering environmental awareness. However, sustainable tourism practices are essential to prevent negative impacts on marine ecosystems.
- Marine Biotechnology: The study of marine organisms has led to innovations with applications in medicine, agriculture, and industry. Marine biotechnology explores the potential of ocean life to address various challenges.
- Ocean Conservation and Restoration: Protecting and restoring marine ecosystems are fundamental aspects of the Blue Economy. Preserving biodiversity, reducing pollution, and establishing marine protected areas are crucial strategies.
- Shipping and Transportation: The movement of goods through shipping contributes significantly to global trade. The Blue Economy encourages the development of sustainable shipping practices, including fuel-efficient vessels and reduced emissions.
- Waste Management and Circular Economy: The Blue Economy promotes waste reduction, recycling, and the transformation of waste materials into valuable resources. This approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy.
Principles of the Blue Economy
The Blue Economy is guided by several fundamental principles:
- Sustainability: Activities within the Blue Economy must be conducted in a manner that maintains the health of marine ecosystems and ensures the longevity of ocean resources.
- Equity and Inclusivity: The benefits of the Blue Economy should be accessible to all, including marginalized communities and small-scale fishers.
- Innovation: Creative solutions and innovative technologies are encouraged to address challenges and drive economic growth.
- Collaboration: Effective management of the Blue Economy requires collaboration among governments, industries, local communities, and scientific experts.
- Science-Based Decision-Making: Policies and practices within the Blue Economy should be informed by scientific research and data.
- Resilience: The Blue Economy aims to create systems that can withstand environmental changes and disturbances.
In the next sections of this blog, we will explore the significance of the Blue Economy in addressing global challenges, its potential benefits, and the steps required to transition towards a more sustainable and inclusive economic model. Ai Cash Heist Review
The Significance of the Blue Economy
1. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Preservation
Our oceans are home to diverse ecosystems that contribute to the health of the planet. The Blue Economy encourages practices that maintain and restore these ecosystems, ensuring the sustainability of marine life and biodiversity.
2. Economic Growth and Job Creation
The Blue Economy holds immense potential for economic growth. Sectors such as fisheries, aquaculture, and tourism have the capacity to generate substantial revenue and provide employment opportunities, particularly in coastal communities.
3. Renewable Energy Sources
The oceans offer vast potential for renewable energy generation through technologies like offshore wind farms, tidal and wave energy, and ocean thermal energy conversion. These sources can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
4. Scientific Exploration and Innovation
The study of marine biology, biotechnology, and other ocean-related fields has led to groundbreaking discoveries with applications in medicine, agriculture, and environmental conservation. The Blue Economy promotes innovation driven by ocean exploration.
5. Food Security
As the global population continues to grow, sustainable fisheries and responsible aquaculture can play a critical role in providing nutritious food sources and addressing food security challenges.
6. Climate Change Mitigation
Healthy oceans act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide. By focusing on sustainable practices and protecting marine ecosystems, the Blue Economy contributes to the fight against climate change.
Key Principles of the Blue Economy
- Sustainability: The Blue Economy emphasizes the responsible use of ocean resources to ensure their availability for future generations.
- Innovation: The concept encourages creative solutions that harness the potential of ocean resources to address various economic, environmental, and social challenges.
- Collaboration: Effective management of the Blue Economy requires cooperation among governments, industries, scientists, and local communities to achieve sustainable outcomes.
- Adaptability: Ocean ecosystems are complex and dynamic. The Blue Economy advocates for adaptable strategies that can evolve to address changing conditions.
- Resilience: Preserving the health of marine ecosystems enhances their resilience to environmental changes and stressors.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Blue Economy holds immense promise, there are challenges that must be addressed to ensure its success. Overfishing, pollution, habitat destruction, and the impacts of climate change pose significant threats to ocean health. Therefore, the Blue Economy must prioritize sustainable practices and conservation efforts to mitigate these challenges. AICourseSite Review
Conclusion: Charting a Sustainable Course
The Blue Economy offers a promising path toward a more sustainable and prosperous future. By recognizing the interconnectedness of economic growth, environmental preservation, and social well-being, we can harness the potential of our oceans while safeguarding their delicate ecosystems. Embracing the principles of sustainability, innovation, collaboration, adaptability, and resilience, we have the opportunity to navigate the uncharted waters of the Blue Economy and shape a world where humanity and nature thrive in harmony.